publications
Authors with ∗ signs contribute equally to the paper.
2025
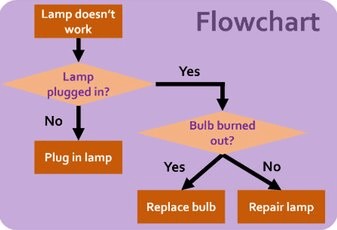
- Beyond End-to-End VLMs: Leveraging Intermediate Text Representations for Superior Flowchart UnderstandingJunyi Ye, Ankan Dash, Wenpeng Yin, and Guiling WangIn Proceedings of the 2025 Annual Conference of the Nations of the Americas Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Long Papers), 2025
Flowcharts are typically presented as images, driving the trend of using vision-language models (VLMs) for end-to-end flowchart understanding. However, two key challenges arise: (i) Limited controllability—users have minimal influence over the downstream task, as they can only modify input images, while the training of VLMs is often out of reach for most researchers. (ii) Lack of explainability—it is difficult to trace VLM errors to specific causes, such as failures in visual encoding or reasoning. We propose TextFlow, addressing aforementioned issues with two stages: (i) Vision Textualizer—which generates textual representations from flowchart images; and (ii) Textual Reasoner—which performs question-answering based on the text representations. TextFlow offers three key advantages: (i) users can select the type of text representations (e.g., Graphviz, Mermaid, PlantUML), or further convert them into executable graph object to call tools, enhancing performance and controllability; (ii) it improves explainability by helping to attribute errors more clearly to visual or textual processing components; and (iii) it promotes the modularization of the solution, such as allowing advanced LLMs to be used in the reasoner stage when VLMs underperform in end-to-end fashion. Experiments on the FlowVQA and FlowLearn benchmarks demonstrate TextFlow’s state-of-the-art performance as well as its robustness. All code will be publicly released.
- Assessing the Creativity of LLMs in Proposing Novel Solutions to Mathematical ProblemsJunyi Ye, Jingyi Gu, Xinyun Zhao, Wenpeng Yin, and Guiling WangIn Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2025
The mathematical capabilities of AI systems are complex and multifaceted. Most existing research has predominantly focused on the correctness of AI-generated solutions to mathematical problems. In this work, we argue that beyond producing correct answers, AI systems should also be capable of, or assist humans in, developing novel solutions to mathematical challenges. This study explores the creative potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in mathematical reasoning, an aspect that has received limited attention in prior research. We introduce a novel framework and benchmark, CreativeMath, which encompasses problems ranging from middle school curricula to Olympic-level competitions, designed to assess LLMs’ ability to propose innovative solutions after some known solutions have been provided. Our experiments demonstrate that, while LLMs perform well on standard mathematical tasks, their capacity for creative problem-solving varies considerably. Notably, the Gemini-1.5-Pro model outperformed other LLMs in generating novel solutions. This research opens a new frontier in evaluating AI creativity, shedding light on both the strengths and limitations of LLMs in fostering mathematical innovation, and setting the stage for future developments in AI-assisted mathematical discovery.
2024
- Preprint
 From Blind Solvers to Logical Thinkers: Benchmarking LLMs’ Logical Integrity on Faulty Mathematical ProblemsMuntasir Rahman*, Junyi Ye*, Wei Yao, Wenpeng Yin, and Guiling WangarXiv preprint arXiv:2410.18921, 2024
From Blind Solvers to Logical Thinkers: Benchmarking LLMs’ Logical Integrity on Faulty Mathematical ProblemsMuntasir Rahman*, Junyi Ye*, Wei Yao, Wenpeng Yin, and Guiling WangarXiv preprint arXiv:2410.18921, 2024Consider the math problem: "Lily received 3 cookies from her best friend yesterday and ate 5 for breakfast. Today, her friend gave her 3 more cookies. How many cookies does Lily have now?” Many LLMs solve this by calculating "1” using the equation "3 - 5 + 3." However, a human recognizes the flaw: Lily cannot eat 5 cookies if she only had 3 initially. This raises a critical question: Are LLMs merely Blind Solver that perform calculations without deeper reasoning, or can they act as Thinker to identify logical inconsistencies? To investigate, we introduce FaultyMath, a benchmark of diverse faulty math problems spanning multiple categories (e.g., algebra, geometry), difficulty levels, and origins of faultiness (e.g., common sense violations, ambiguity, contradictions). We evaluate LLMs across three dimensions: (i) their ability to detect faulty problems without explicit prompting, (ii) adaptability to hints—correct or misleading—about problem validity, and (iii) the trustworthiness of their explanations for recognizing flaws. Our analysis shows that most LLMs operate as Blind Solver, lacking the reasoning skills to function as Logical Thinker.
- DataFrame QA: A Universal LLM Framework on DataFrame Question Answering Without Data ExposureJunyi Ye, Mengnan Du, and Guiling WangIn The 16th Asian Conference on Machine Learning (Conference Track), 2024
This paper introduces DataFrame Question Answering (QA), a novel task that utilizes natural language processing (NLP) models to generate Pandas queries for information retrieval and data analysis on dataframes, emphasizing safe and non-revealing data handling. Specifically, our method, leveraging a large language model (LLM), which solely relies on dataframe column names, not only ensures data privacy but also significantly reduces the context window in the prompt, streamlining information processing and addressing major challenges in LLM-based data analysis. We propose DataFrame QA as a comprehensive framework that includes safe Pandas query generation and code execution. Various LLMs are evaluated on the renowned WikiSQL dataset and our newly developed UCI-DataFrameQA, tailored for complex data analysis queries. Our findings indicate that GPT-4 performs well on both datasets, underscoring its capability in securely retrieving and aggregating dataframe values and conducting sophisticated data analyses. This approach, deployable in a zero-shot manner without prior training or adjustments, proves to be highly adaptable and secure for diverse applications.
- DySTAGE: Dynamic Graph Representation Learning for Asset Pricing via Spatio-Temporal Attention and Graph EncodingsJingyi Gu*, Junyi Ye*, Ajim Uddin, and Guiling WangIn Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, Brooklyn, NY, USA, 2024
Current GNN-based asset price prediction models often focus on a fixed group of assets and their static relationships within the financial network. However, this approach overlooks the reality that the composition of asset pools and their interrelationships evolves over time, necessitating the development of a flexible framework capable of adapting to this dynamism. Accordingly, we propose DySTAGE, a framework with a universal formulation that transforms asset pricing time series into dynamic graphs, accommodating asset addition, deletion, and changes in correlations. Our framework includes a graph learning model specifically designed for this purpose. In our framework, assets at various historical time steps are structured as a sequence of dynamic graphs, where connections between assets reflect their long-term correlations. DySTAGE effectively captures both topological and temporal patterns. The Topological Module deploys Asset Influence Attention to learn global interrelationships among assets, further enhanced by Asset-wise Importance Encoding, Pair-wise Spatial Encoding, and Edge-wise Correlation Encoding. Meanwhile, the Temporal Module encapsulates node representations across the temporal dimension via the attention mechanism. We validate our approach through extensive experiments using three different real-world stock pricing data, demonstrating that DySTAGE surpasses popular benchmarks in return prediction, and offers profitable investment strategies. The code is publicly available under NJIT FinTech Lab’s GitHub1.
- Adaptive and Explainable Margin Trading via Large Language Models on Portfolio ManagementJingyi Gu*, Junyi Ye*, Guiling Wang, and Wenpeng YinIn Proceedings of the 5th ACM International Conference on AI in Finance, Brooklyn, NY, USA, 2024
Recent strategies for portfolio management often lack flexibility to adjust funds between long and short positions throughout trading periods. This prevents adapting portfolios to the market, which mitigates risks and seizes opportunities. To address these gaps, we propose an adaptive and explainable framework that integrates Large Language Models (LLMs) with Reinforcement Learning (RL) for dynamic long-short position adjustment in response to evolving market conditions. This approach leverages the recent advancements in LLMs for processing unstructured data and their capacity for explainable reasoning. The framework includes two stages: an Explainable Market Forecasting/Reasoning Pipeline, and a Position Reallocation stage. The Market Forecasting/Reasoning Pipeline allows various LLMs to learn market trends from diverse external data sources and determine optimal adjustment ratios with a clear reasoning path. The Portfolio Reallocation stage interacts with the sequential trading process from a pre-trained RL model to enhance decision-making and transparency. Our framework is flexible to accommodate various external data sources from microeconomics to macroeconomics data, diverse data types including time series and news text, along with multiple LLMs. Experiments demonstrate that our framework effectively achieves three times the return and doubles the Sharpe ratio compared to benchmarks. All the data and code are publicly available under NJIT FinTech Lab’s GitHub1.
- AODS
 High Resolution Solar Image Generation Using Generative Adversarial NetworksAnkan Dash, Junyi Ye, Guiling Wang, and Huiran JinAnnals of Data Science, 2024
High Resolution Solar Image Generation Using Generative Adversarial NetworksAnkan Dash, Junyi Ye, Guiling Wang, and Huiran JinAnnals of Data Science, 2024We applied Deep Learning algorithm known as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to perform solar image-to-image translation. That is, from Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO)/Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) line of sight magnetogram images to SDO/Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) 0304-Å images. The Ultraviolet (UV)/Extreme Ultraviolet observations like the SDO/AIA 0304-Å images were only made available to scientists in the late 1990s even though the magnetic field observations like the SDO/HMI have been available since the 1970s. Therefore, by leveraging Deep Learning algorithms like GANs we can give scientists access to complete datasets for analysis. For generating high resolution solar images, we use the Pix2PixHD and Pix2Pix algorithms. The Pix2PixHD algorithm was specifically designed for high resolution image generation tasks, and the Pix2Pix algorithm is by far the most widely used image to image translation algorithm. For training and testing we used the data for the year 2012, 2013 and 2014. After model training, we evaluated the model on the test data. The results show that our deep learning models are capable of generating high resolution (1024 × 1024 pixels) SDO/AIA0304 images from SDO/HMI line of sight magnetograms. Specifically, the pixel-to-pixel Pearson Correlation Coefficient of the images generated by Pix2PixHD and original images is as high as 0.99. The number is 0.962 if Pix2Pix is used to generate images. The results we get for our Pix2PixHD model is better than the results obtained by previous works done by others to generate SDO/AIA 0304 images. Thus, we can use these models to generate AIA0304 images when the AIA0304 data is not available which can be used for understanding space weather and giving researchers the capability to predict solar events such as Solar Flares and Coronal Mass Ejections. As far as we know, our work is the first attempt to leverage Pix2PixHD algorithm for SDO/HMI to SDO/AIA0304 image-to-image translation.
- BIOTC
 Establishing a Baseline for Evaluating Blockchain-Based Self-Sovereign Identity Systems: A Systematic Approach to Assess Capability, Compatibility and InteroperabilityWei Yao, Wenlu Du, Jingyi Gu, Junyi Ye, Fadi P Deek, and Guiling WangIn Proceedings of the 2024 6th Blockchain and Internet of Things Conference, 2024
Establishing a Baseline for Evaluating Blockchain-Based Self-Sovereign Identity Systems: A Systematic Approach to Assess Capability, Compatibility and InteroperabilityWei Yao, Wenlu Du, Jingyi Gu, Junyi Ye, Fadi P Deek, and Guiling WangIn Proceedings of the 2024 6th Blockchain and Internet of Things Conference, 2024Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) is an evolving means of identity management that aims to give individuals more control over their digital identities and personal data rather than relying on third-party organizations or government authorities. Blockchain technology has the potential to strengthen SSI significantly by providing a secure and decentralized method towards managing and storing personal data, rendering them resistant to tampering and also enhancing their privacy. Given the diversity of blockchain-based SSI platforms, including Sovrin, uPort, and Hyperledger Indy, it is essential to have a consistent approach to evaluate the different SSI systems consistently. This paper offers guidelines for building systematic architecture and defining comprehensive internal interactions for a complete SSI system, thereby providing a framework for routine evaluation and analysis of an existing SSI platform and establishing base standards for assessing capability, compatibility and interoperability of SSI systems. Accordingly, the paper also reports on comprehensive experiments over many existing blockchain-based SSI systems using a multi-layered approach.
- Preprint
 From Factor Models to Deep Learning: Machine Learning in Reshaping Empirical Asset PricingJunyi Ye*, Bhaskar Goswami*, Jingyi Gu*, Ajim Uddin, and Guiling WangarXiv preprint arXiv:2403.06779, 2024
From Factor Models to Deep Learning: Machine Learning in Reshaping Empirical Asset PricingJunyi Ye*, Bhaskar Goswami*, Jingyi Gu*, Ajim Uddin, and Guiling WangarXiv preprint arXiv:2403.06779, 2024This paper comprehensively reviews the application of machine learning (ML) and AI in finance, specifically in the context of asset pricing. It starts by summarizing the traditional asset pricing models and examining their limitations in capturing the complexities of financial markets. It explores how 1) ML models, including supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning, provide versatile frameworks to address these complexities, and 2) the incorporation of advanced ML algorithms into traditional financial models enhances return prediction and portfolio optimization. These methods can adapt to changing market dynamics by modeling structural changes and incorporating heterogeneous data sources, such as text and images. In addition, this paper explores challenges in applying ML in asset pricing, addressing the growing demand for explainability in decision-making and mitigating overfitting in complex models. This paper aims to provide insights into novel methodologies showcasing the potential of ML to reshape the future of quantitative finance.
- IEEE Access
 A Review of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Its Applications in a Wide Variety of Disciplines: From Medical to Remote SensingAnkan Dash, Junyi Ye, and Guiling WangIEEE Access, 2024
A Review of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Its Applications in a Wide Variety of Disciplines: From Medical to Remote SensingAnkan Dash, Junyi Ye, and Guiling WangIEEE Access, 2024We look into Generative Adversarial Network (GAN), its prevalent variants and applications in a number of sectors. GANs combine two neural networks that compete against one another using zero-sum game theory, allowing them to create much crisper and discrete outputs. GANs can be used to perform image processing, video generation and prediction, among other computer vision applications. GANs can also be utilised for a variety of science-related activities, including protein engineering, astronomical data processing, remote sensing image dehazing, and crystal structure synthesis. Other notable fields where GANs have made gains include finance, marketing, fashion design, sports, and music. Therefore in this article we provide a comprehensive overview of the applications of GANs in a wide variety of disciplines. We first cover the theory supporting GAN, GAN variants, and the metrics to evaluate GANs. Then we present how GAN and its variants can be applied in twelve domains, ranging from STEM fields, such as astronomy and biology, to business fields, such as marketing and finance, and to arts, such as music. As a result, researchers from other fields may grasp how GANs work and apply them to their own study. To the best of our knowledge, this article provides the most comprehensive survey of GAN’s applications in different field.
2023
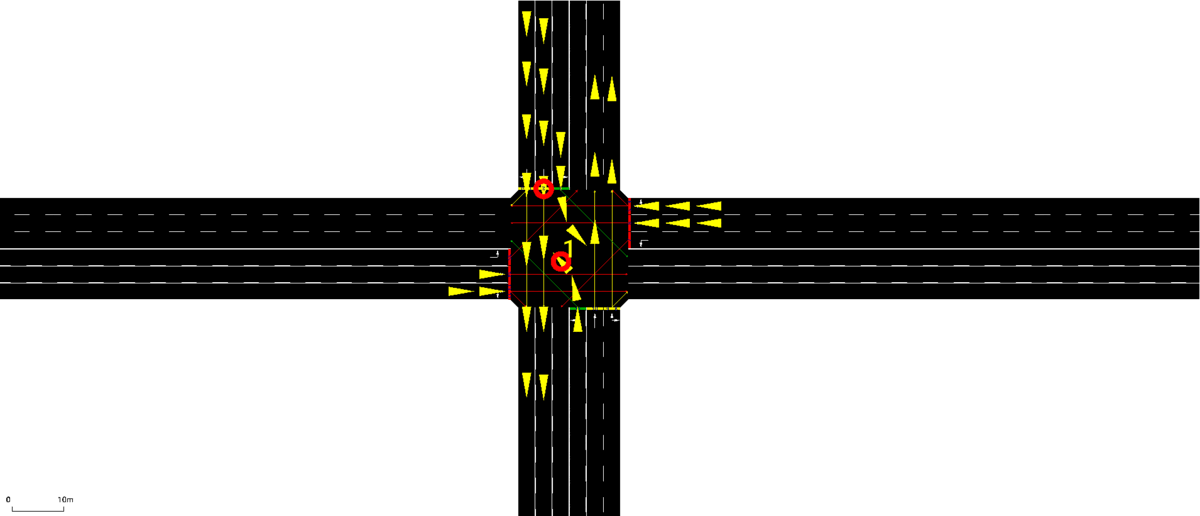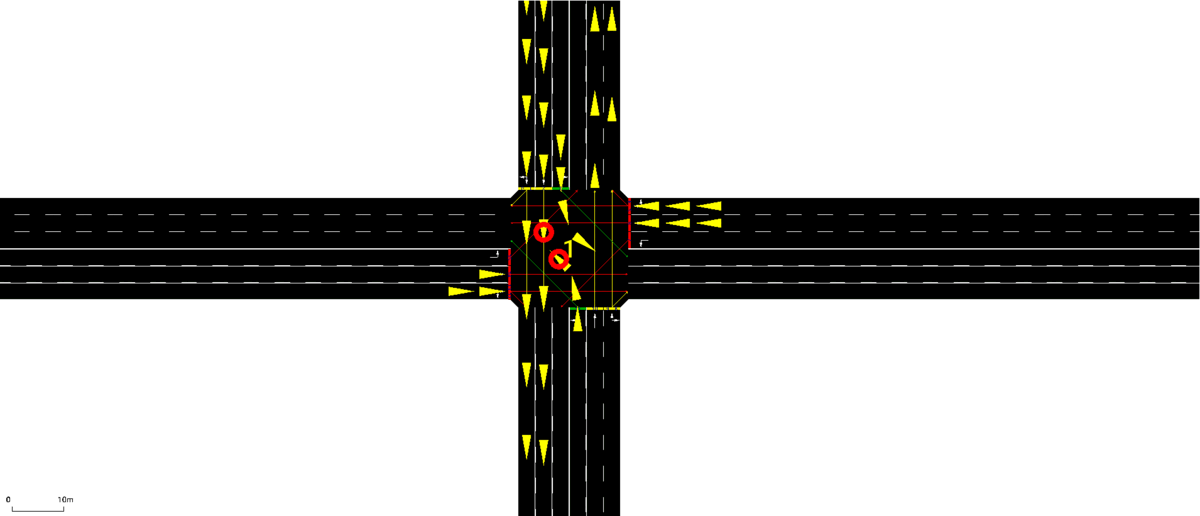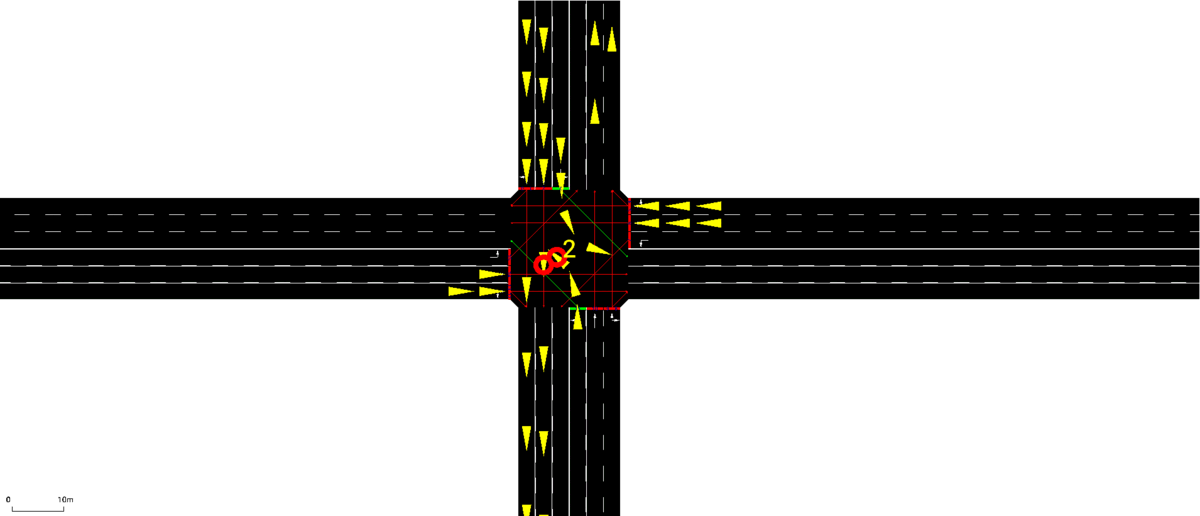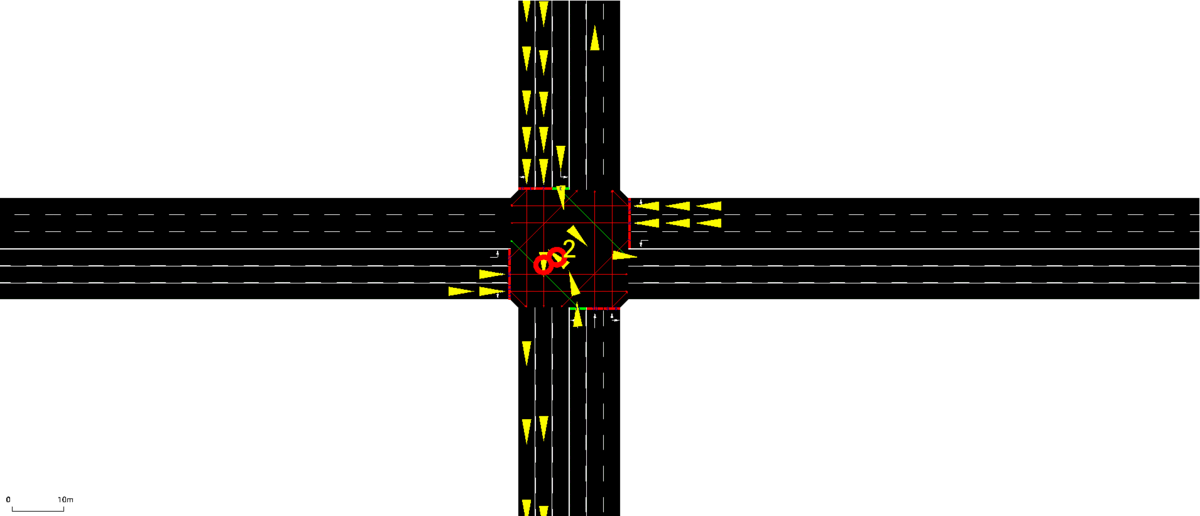
- SafeLight: A Reinforcement Learning Method toward Collision-Free Traffic Signal ControlWenlu Du, Junyi Ye, Jingyi Gu, Jing Li, Hua Wei, and Guiling WangProceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Jun 2023
Traffic signal control is safety-critical for our daily life. Roughly one-quarter of road accidents in the U.S. happen at intersections due to problematic signal timing, urging the development of safety-oriented intersection control. However, existing studies on adaptive traffic signal control using reinforcement learning technologies have focused mainly on minimizing traffic delay but neglecting the potential exposure to unsafe conditions. We, for the first time, incorporate road safety standards as enforcement to ensure the safety of existing reinforcement learning methods, aiming toward operating intersections with zero collisions. We have proposed a safety-enhanced residual reinforcement learning method (SafeLight) and employed multiple optimization techniques, such as multi-objective loss function and reward shaping for better knowledge integration. Extensive experiments are conducted using both synthetic and real-world benchmark datasets. Results show that our method can significantly reduce collisions while increasing traffic mobility.
- ICDEW
 Prediction with Time-Series Mixer for the S&P500 IndexJunyi Ye, Jingyi Gu, Ankan Dash, Fadi P. Deek, and Guiling Grace WangIn 2023 IEEE 39th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW), Jun 2023
Prediction with Time-Series Mixer for the S&P500 IndexJunyi Ye, Jingyi Gu, Ankan Dash, Fadi P. Deek, and Guiling Grace WangIn 2023 IEEE 39th International Conference on Data Engineering Workshops (ICDEW), Jun 2023As an essential US economic indicator, the S&P500 Index is used to assess the current state of market performance and gauge the economy’s future course. However, stock market index prediction is challenging due to its nonlinearity and inherently volatile character. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and their variants are de facto standards for sequence modeling. Recently, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) and attention-based networks, such as dilated casual convolutions and Transformers, have also become popular in time series forecasting. In this paper, we report on the design of a Time-Series Mixer (TS-Mixer) architecture based on MLP-Mixer, an all-MLP architecture for time series forecasting. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first implementation of MLP-Mixer-based architecture for sequence modeling. Modern deep learning models are increasingly built to handle univariate time series data. They generally pay attention to analyzing temporal dependencies while ignoring the relationship among features. The proposed architecture is specifically created for multivariate time series forecasting to capture temporal feature interactions while simultaneously learning feature correlations. To accomplish this, the proposed Time-Feature Mixer contains two types of MLP layers: feature mixer and temporal mixer. The feature mixer is applied independently to each data point to capture the correlation among features. In contrast, the temporal mixer extracts temporal dependency (trend, seasonal, cyclical, or random characteristics) of each feature across the whole input sequence. Compared to prevalent neural networks in sequence modeling, TS-Mixer exhibits competitive performance regarding S&P500 Index prediction.